Should I use 10 AWG or 12 AWG Wires for solar?
When choosing between 10 AWG and 12 AWG wires for solar installations, it’s essential to consider factors such as current capacity, voltage drop, and wire length.
10 AWG wires have a larger diameter and can handle higher current loads, making them suitable for systems with higher amperage requirements.
12 AWG wires, on the other hand, are thinner and more cost-effective but have a lower current carrying capacity.
To make the best choice, calculate the required current capacity and acceptable voltage drop for your solar installation.
If the voltage drop remains within acceptable limits and the current capacity is sufficient using 12 AWG wires, they may be the more economical choice.
However, if your system requires a higher current capacity or a longer wire run, 10 AWG wires would be more appropriate to ensure system efficiency and safety.
Importance of choosing the correct wire gauge for solar installations
Selecting the correct wire gauge is essential for solar panel installations.
Voltage drop and energy losses are minimized when the appropriate wire gauge is chosen, resulting in a smooth and efficient flow of electricity within the solar panel system.
However, choosing the wrong wire gauge can lead to electrical issues, safety hazards, and system failures, which can be costly to repair or replace.
Therefore, it is important to carefully consider the wire gauge selection process to ensure the safe and efficient operation of your solar panel system.
Basics of wire gauge
Electrical wire diameter is measured using the American Wire Gauge (AWG) standard system.
The higher the AWG number, the thinner the wire diameter. This relationship is crucial because the thickness of the wire affects its current-carrying capacity and resistance.
For example, a 10 AWG wire can carry more current than a 12 AWG wire because it has a larger diameter and lower resistance.
Wire gauge plays a significant role in determining resistance, voltage drop, and heat production within a solar panel system.
Wires with a larger diameter offer lower resistance, resulting in decreased voltage drop and minimized energy losses. However, these thicker wires can produce more heat, potentially leading to safety concerns.
Choosing a wire that is too thin may result in voltage drop and energy losses while selecting one that is excessively thick can raise costs and cause compatibility issues with connectors.
As such, it is critical to comprehend the AWG system and pick the right wire gauge to ensure the optimal performance and success of your solar installation.
Factors determining wire gauge selection
Distance between solar panels and charge controller or inverter
The wire gauge used in solar installations is heavily influenced by the distance between the panels and the charge controllers or inverters.
Wires need to be thicker to prevent energy loss and voltage drop over greater distances. This is because voltage drops and system efficiency decreases with increasing distance because of increased wire resistance.
Because of this, especially for greater distances, it is crucial to select a wire gauge thick enough to reduce resistance and voltage drop. Your solar panel system’s performance and your ability to reap its benefits depend on the wire gauge you choose.
Maximum current flow
Maximum current flow is another important factor in determining the required wire gauge in a solar panel system.
Wires need to be thicker when the current running through them increases to prevent overheating and voltage drop. Because of their lower resistance, the thicker wires can take in more current without overheating.
When selecting the wire gauge, it is crucial to consider the maximum current flow to ensure the wire can handle the load.
If a wire is too thin for the current flow, it will overheat and potentially cause the system to fail. Your solar panel system’s safety and performance depend on your ability to correctly select the wire gauge.
Voltage drop considerations
The wire gauge of a solar panel system must be chosen with voltage drop in mind.
When electricity travels along a wire with resistance, energy is lost and the voltage drops. Since thicker wires have less resistance, voltage drop and energy losses are reduced.
Voltage drops in solar installations can reduce system efficiency, leading to lost power and less energy produced.
For this reason, it is crucial to select a wire gauge thick enough to reduce voltage drop and energy losses, particularly over greater distances.
You can maximize the effectiveness of your solar panel system and its output by carefully considering the wire gauge you use.
Temperature and environmental factors
Temperature and environmental factors are other important considerations when selecting the appropriate wire gauge for a solar panel system.
Wires exposed to high temperatures or corrosive environments require thicker insulation to prevent damage and ensure safe and efficient operation.
High temperatures can cause wires to expand and contract, which can lead to mechanical stress and damage to the insulation.
Corrosive environments can cause oxidation and corrosion of the wire, which can weaken the wire and reduce its current-carrying capacity.
Therefore, it is essential to choose a wire gauge that is thick enough to withstand the temperature and environmental conditions of the installation site.
By selecting the appropriate wire gauge, you can ensure that your solar panel system operates safely and efficiently, even in harsh environmental conditions.
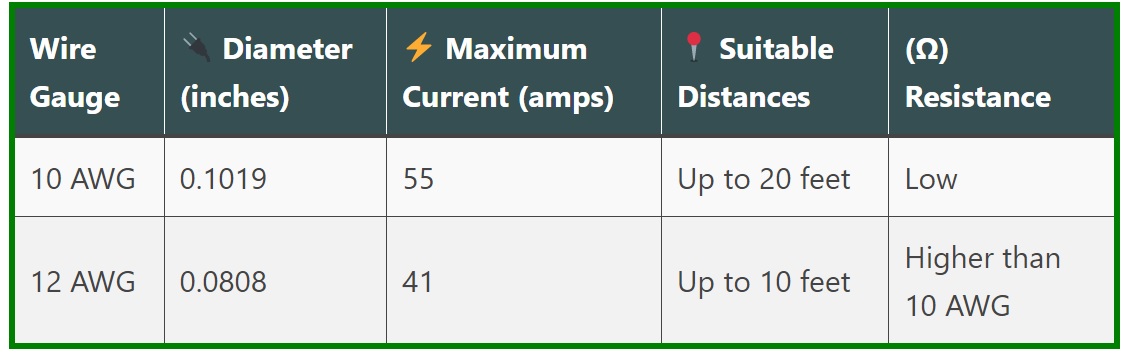
10 AWG vs. 12 AWG for solar installations
| Wire Gauge | 🔌 Diameter (inches) | ⚡ Maximum Current (amps) | 📍 Suitable Distances | (Ω) Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 AWG | 0.1019 | 55 | Up to 20 feet | Low |
| 12 AWG | 0.0808 | 41 | Up to 10 feet | Higher than 10 AWG |
Overview of 10 AWG wire
10 AWG wire is commonly used in solar installations due to its excellent properties.
This wire can handle up to 55 amps of current and has a thickness of 0.1019 inches. As a result, it can be used in a variety of solar power setups, particularly at distances of up to 20 feet.
Because of the low resistance provided by 10 AWG wire, voltage drop, and energy losses are kept to a minimum.
It’s also simple to use, making it a favorite among installers. Because of its low cost and widespread availability, 10 AWG wire is a popular choice among DIYers looking to save money on wiring.
In general, solar installations up to 20 feet in length can safely rely on 10 AWG wires. Its thickness, low resistance, and ready availability make it popular among installers and homeowners alike.
Overview of 12 AWG wire
12 AWG wire is another popular alternative for smaller solar systems or shorter distances.
Because of its smaller diameter of 0.0808 inches, it is thinner than the 10 AWG wire. However, with a maximum current capacity of 41 amps, it remains a feasible alternative for many solar setups at distances of up to 10 feet.
Despite having more resistance than 10 AWG wire, 12 AWG wire is still a suitable alternative for many solar projects. Because of its inexpensive cost and widespread availability, it is a popular choice among homeowners looking to save money on costly improvements.
When it comes to wiring photovoltaic panels across short distances, 12 AWG wire is a good choice. It is simple to use and affordable, making it popular among installers and homeowners alike.
Importance of manufacturer guidelines and local electrical codes
Manufacturer specifications for wire sizing
Manufacturers provide guidelines for wire sizing based on their product specifications. Following these guidelines ensures that the solar panel system functions safely and efficiently.
Local electrical codes and regulations
Local electrical codes and regulations govern the installation of electrical systems, including solar panel systems. Compliance with these codes and regulations ensures the safety and protects against legal liabilities.
Ensuring a safe and efficient solar installation
To ensure a safe and efficient solar installation, it’s crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines and local electrical codes. Consultation with professionals, such as electricians or solar panel installers, can also provide valuable insight into proper wire gauge selection.
Conclusion
Choosing the right wire gauge is crucial for the security and performance of solar panel systems. It lessens the likelihood of system failures, energy waste, and voltage drops.
Proper wire gauge selection and installation of solar panel systems are ensured by consulting with professionals and adhering to manufacturer guidelines and local electrical codes.
Wire gauges for solar installations must be chosen with distance, current flow, voltage drop, temperature, and environmental factors in mind. A safe and effective solar panel system can be the result of giving due consideration to the aforementioned considerations.