Solar Power Towers (A Comprehensive Guide)
There’re many ways to produce electricity from solar energy. The most common is direct production using solar photovoltaic.
But did you know that concentrating solar thermal technology can also be used to indirectly produce electricity in a clean and greener way?
Solar power towers are the most advanced concentrating solar power technology with the capacity to continually produce huge amounts of power.
This indirect solar power production method uses sunlight concentrating mirrors and a solar power tower to produce clean electricity for residential and commercial use.
Here's a detailed look at solar power towers, so you can understand the great potential they hold for ramping up solar power production.
What is a Solar Power Tower?
Solar power tower is a solar power production technology that uses large flat or curved mirrors (heliostats) to track and reflect the sun's rays onto a receiver mounted on a tall tower.
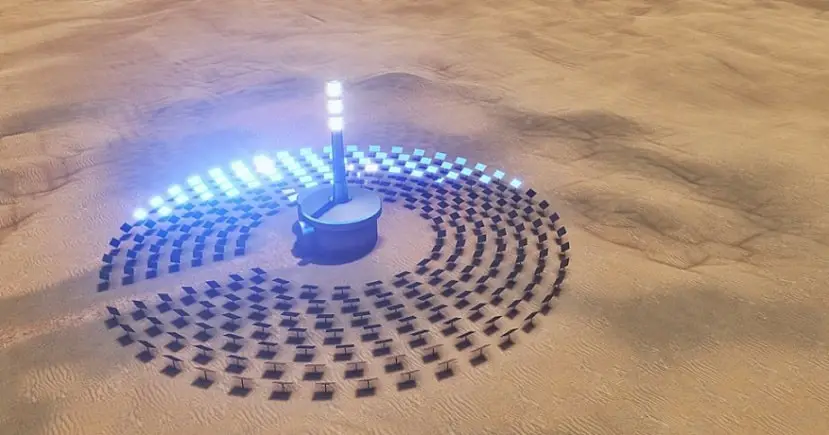
Solar power towers are also known as central towers or simply solar towers.
Electricity generation using solar power towers follows the concentrating solar power technology.
The beams that are focused on the tower generate heat, which is used to generate steam. The steam runs a turbine to generate electricity.
With their high and constant power production capacity, solar power towers are a very viable source of clean energy throughout the world.
Solar Power Tower: The design
Sun tracking mirrors (heliostats, solar reflectors, solar concentrators)
Solar tracking mirrors are one of the vital components of solar tower design. They reflect sunlight to a specific point on the solar tower creating a solar flux.
Hundreds to thousands of mirrors are required for one solar tower, which means that solar power tower projects require quite an amount of space.
Solar power projects use parabolic mirrors most commonly since, due to their curvature, they perform a great job at concentrating sunlight.
To reduce costs, flat mirrors can also be used, but they need to be tilted at a specific angle to focus the sun's rays on the solar power tower.
Solar collector mirrors near the solar power are more efficient at focusing sunlight and receive less power loss due to the shorter distance that lights beams travel.
On the other hand, collector mirrors far from the solar tower must focus the beams at a longer distance, resulting in possible energy loss.
In addition, mirrors far from the tower are at risk of being shaded by the adjacent mirrors, so they must be spaced out appropriately.
The tower
This is usually the large tall steel and concrete structure supporting the heat receiver and housing the thermal liquid.
Towers as high as 100m to 200m are preferred since they require large, denser heliostats that take up less land space and eliminate shading problems.
In a typical plant, the tower is placed in a central location where it’s easier to focus the beams from the sunlight tracking mirrors.
Solar thermal components
Solar thermal fluids used in solar power towers have changed over time.
Steam was initially used as a means of capturing heat going into the tower. Later, liquid sodium was introduced as the thermal fluid for these towers.
Recently, a mixture of molten salts, precisely potassium nitrate, and sodium nitrate, is used.
Molten salts are preferred for their high heat-carrying capacity, wide availability, and low cost.
Heat transfer liquid pipes carry the working liquids from the receiver on the tower to the storage/ heat exchange tanks. Most solar power towers are two-tank thermal storage systems.
One tank stores the cold liquid that has already transferred its heat content, while the other stores the liquid that has just been heated.
The control system
A power station needs a control system to manage how the heliostats and the solar power tower function. The control system encompasses the communication components and the alarms.
The control system is like an interface where you are able to interact with everything that’s happening in the solar power tower plant.
The cooling system
Solar power towers are installed in scorching desert conditions. It is for this reason that power towers need to be cooled if they’re to function optimally.
Water or air can be used to cool the solar power tower, but air cooling is more economical in desert conditions where ground or surface water isn’t available.
Solar power tower plants should be designed in a way that reduces raw material and installation costs.
Solar Power Tower VS Solar Photovoltaic
| Factor | Solar Power Tower | Solar Photovoltaic |
| Method of electricity generation | Uses solar heat to produce steam that's, in turn, runs a turbine to produce electricity | Direct conversion of light into electricity |
| Efficiency | Low efficiency as there’s limiting factors such as wind | Standard efficiency since there’re also problems such as shading |
| Power production reliability | Highly reliable as electricity production continues even at night | Insufficiently reliable as electricity can only be produced during the day |
| Cost | 6,000 to $10,000 per kW with 6-15 hours of operation | Around $1,000 per kW |
| Solar collecting structures | Large concentrating mirrors | Solar panels |
| Energy storage systems | Thermal liquids | Solar rechargeable batteries |
| Design complexity | A high number of complex components need to be harmonized for optimum production | Easier to build since the solar panels just need to be mounted in a strategic place |
How do Solar Power Towers Work?
Solar power towers generate electricity using concentrated solar power technology.
The working principle
The collector mirrors harness the sun's rays and focus them on the solar power tower. The concentrated beams form a solar flux that acts as a heat source.
A heat transfer liquid is used to harness the concentrated solar energy and transfer it to the steam-generating tank. The produced steam runs a generator turbine (installed on the ground) to generate clean electricity.
Solar power towers are likened to external heat engines since the heat source is separate from the thermal liquid.
The central section of the solar power plant can get temperatures as high as 1000°C. While this means that more power can be generated through thermal means, it also creates a serious hazard, as we'll discuss later in this article.
Solar power towers are capable of producing electricity for both home and commercial applications.
Lately, there's been more interest in utility-sized solar power tower projects that can produce high amounts of electricity to power several commercial buildings.
Major solar power tower projects
| Name of the project | Location | Power production capacity (MW) | Number of collectors | Height of tower in (ft) | Height of tower in (m) |
| Ivanpah | Mojave Desert, California | 392 | 173,500 | 459 | 139.9 |
| Crescent Dunes | Tonopah, US | 110 | 10,347 | 656 | 200 |
| Ashalim power station | Negev Desert, Israel | 121 | 50,600 | 853 | 260 |
| Shouhang Dunhuang | Dunhuang, China | 100 | 1200 | 722 | 220 |
| Gemasolar,Thermosolar plant. | Seville, Spain | 19.9 | 2650 | 460 | 140 |
| PS20 | Sanlúcar la Mayor, Spain | 20 | 1255 | 541 | 165 |
Pros of solar power towers
Production of cleaner and greener energy
Solar-power towers are considered clean and green power sources if they rely solely on the sun for electricity production.
A solar tower plant may burn fossil fuels to jump-start steam production, which sometimes compromises the ‘clean and green’ aspects of the power produced.
But even so, the pollution is still lower compared to conventionally burning fossil fuels.
Value addition on dry, bare lands
Most solar power plants are set up in deserts, which means that the dry bear land is put into better use.
Considering that these plants can generate a considerable amount of power, deserts can now be turned into green energy production hubs.
Large amounts of solar power are produced daily
The power production capacity of solar power towers is relatively higher when compared to conventional methods of producing electricity.
By simply increasing the number of heliostats, you can even create a utility-sized plant and generate large amounts of electricity.
Power generated by the plant can always be fed into the grid and distributed to nearby facilities.
Constant electricity production
As long as there's sunlight, solar power tower plants will produce electricity.
Luckily, most of these plants are set up in deserts where the sun is always shining, so power production happens continuously.
Cons of solar power towers
Risk of killing birds
The temperatures around solar power towers are extremely high. If birds pass over this region of very high temperatures, their feathers can be burnt up, or worse, they can be melted instantly on the spot.
Such scenarios happened during the test phase of the Ivanpah solar power tower project that a strategy of spacing out the mirrors was invented.
Impressively, by ensuring that no four concentrating mirrors focus the sunlight beams on one spot, incidences of birds killing were stopped.
Greenhouse gas emissions
A solar power tower plant is supposed to be pollution-free since it harnesses the energy from the sun to produce electricity.
However, some solar-powered power tower plants require fossil fuel burning to bring the structures up to the needed operating temperature to produce steam.
A consequence of this can be increased greenhouse gas emissions, which are clearly hazardous to the environment.
Space intensive
Heliostats are required in large numbers to focus sunlight on the tower, and they obviously take up a lot of space.
As a result, solar power towers are restricted to places with extensive tracts of land, such as deserts.
If this seems like a less important issue, below is the more serious downside.
Ecosystem disturbances
In order to get the best performance from solar collector mirrors, they must be cleaned often. The local ecosystem may be affected if groundwater or surface water from the area is used for this purpose.
Despite the fact that solar power towers are built in deserts, wild animals may also lose their habitat because some plants need to be cleared.
Future Trends for Solar Power Towers
Development of cheap heliostats
A high number of solar collector mirrors are needed for a solar power tower to produce a considerable amount of energy.
For this reason, there's a need to produce cheap heliostats to reduce the material cost and the overall cost for solar power tower projects.
Design improvements for the thermal fluid systems
An upgrade from the current two tanks thermal systems to a one-tank system with thermal fillers and oxygen blankets is needed.
Improving the thermal fluid systems will enhance the efficiency of solar power towers and consequently reduce the cost incurred in operating this solar generating equipment.
Use of supercritical CO2 and supercritical steam cycles
Supercritical CO2 is CO2 heated and pressurized above its critical point.
Due to its high heat-carrying capacity, high density, low viscosity, and low cost, supercritical CO2 is a superb working fluid for solar power towers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What salt is used in solar power towers?
Molten salt, usually a mixture of potassium nitrate and sodium nitrate is used as the heat-carrying fluid in solar power towers.
The molten salts are mixed in well-calculated proportions to get the maximum heat capacity from the mixture.
Does a solar power tower produce electricity when there's no sunshine?
Thanks to the molten salt that stores the heat during peak production, solar power towers can produce electricity even when the sun isn't shining.
Even so, solar power towers are installed in deserts where the sun is expected to shine most of the time.
What's the ideal location to install a solar power tower?
Conclusion
Solar towers are an excellent source of energy thanks to the highly reliable concentrated solar power (CSP) technology.
Although solar power tower projects are only feasible in areas with enough free land, the power produced can be fed into the grid and used for residential and commercial purposes.
By utilizing solar power tower plants, we can generate huge amounts of electricity while at the same time saving the environment from pollution.
Solar power towers have their own shortcomings, but with the proposed innovations, these problems will most likely be alleviated.







